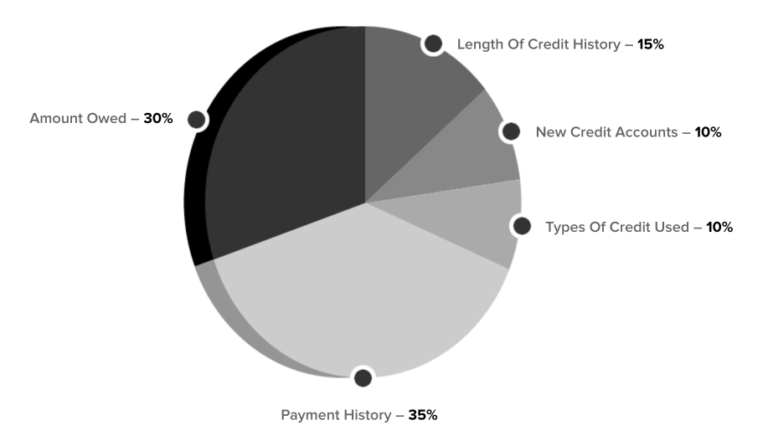
Your credit report is the basis of your FICO score. Your report details your credit history as it has been reported to the credit reporting agency by lenders who have extended credit to you, by court records, and by you. The FICO score analyzes information from the trade line, inquiry, public record, and collection sections of your credit report. A FICO score evaluates five main categories of information in your credit report and compares this information to the patterns in hundreds of thousands of other credit reports. These five categories are, in order of importance:
Payment History - What Is Your Payment Track Record?
Risk predictors here are:
- Severity : how bad are the delinquencies?
- Recency : how recent are they?
- Frequency: how many delinquencies occurred?

Amounts Owed - How Much Is Too Much?
Risk predictors here are:
- Large outstanding balances
- The ratio of balances to credit limits

Length of Credit History - How established is yours?
Risk predictors here are:
New Credit - Are you taking on more debt?
Risk predictors here are:
- Number of inquiries and new account openings
Types of Credit in Use - Is it a healthy mix?
Risk predictors here are:
- Number of credit lines reported for each type: bankcards, retail, department store cards, installment loans, etc.
More Educational Resources

Work directly with the owner, Certified in Credit Restoration, Credit Score Models and Optimizations.
Work directly with the owner, Certified in Credit Restoration, Credit Score Models and Optimizations.

Work directly with the owner, Certified in Credit Restoration, Credit Score Models and Optimizations.
View more from our blog
Credit Scoring Education - How Are Scores Calculated?


